Introduction
Imagine the discomfort of a small, persistent tear in the most sensitive area of your body. Anal fissures, though often overlooked, can cause significant pain and distress. These small, painful cracks or tears in the lining of the anal canal are commonly linked to various anal fissure causes. They can make everyday activities, including bowel movements, incredibly uncomfortable.
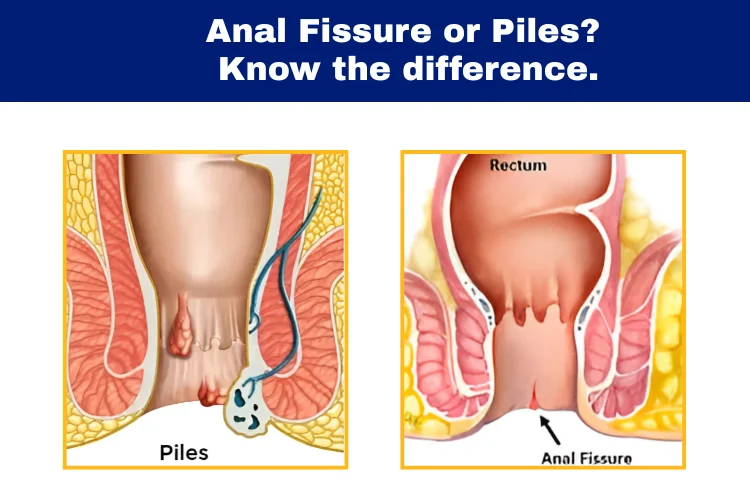
Anal fissures are defined as tiny tears in the delicate skin of the anal canal, leading to symptoms such as sharp pain, itching, and bleeding during and after bowel movements. These fissures often result from various anal fissure causes, such as stress or trauma to the anal mucosa. The resulting tear can be quite painful and slow to heal, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing the underlying anal fissure causes.
Understanding the causes of anal fissures is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. By identifying and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to these fissures, individuals can better manage their condition and avoid recurrence. Anal fissure causes can range from chronic constipation and diarrhea to more complex issues like inflammatory bowel diseases and trauma from childbirth or sexual activity. Recognizing these causes not only aids in treating existing fissures but also helps in implementing preventive measures to avoid future occurrences.
A thorough understanding of anal fissure causes empowers individuals to take proactive steps in their health management. Effective treatment often requires addressing the root causes, whether through dietary changes, improved hydration, or managing underlying health conditions. This proactive approach ensures that individuals receive the most comprehensive care and support, ultimately leading to a better quality of life.
Common Causes of Anal Fissures

Chronic Constipation
Chronic constipation is one of the most common anal fissure causes. When individuals experience ongoing constipation, they often pass hard, dry stools that can cause trauma to the delicate lining of the anal canal. The friction and pressure from these hard stools can create small tears or fissures in the anal mucosa. Additionally, the act of straining during bowel movements further exacerbates this issue. Straining increases the pressure within the anal canal, making it more likely for these tiny tears to occur and persist, leading to chronic discomfort and pain.
Diarrhea
Frequent, loose stools are another significant cause of anal fissures. Diarrhea can irritate and inflame the anal region due to its frequent passage and the high moisture content of the stools. This irritation can cause the skin around the anus to become sensitive and prone to tearing. Prolonged or severe diarrhea can worsen this condition, leading to persistent inflammation and an increased risk of developing anal fissures. The constant irritation from frequent bowel movements disrupts the natural healing process, making fissures more difficult to resolve.
Childbirth
Childbirth, particularly vaginal delivery, is a notable cause of anal fissures. The process of childbirth can exert significant pressure and trauma on the anal area, leading to fissures. During delivery, the anal region can be stretched or torn, especially in cases of difficult labor or the use of an episiotomy. An episiotomy, which is a surgical incision made to facilitate delivery, can inadvertently increase the risk of developing anal fissures by compromising the integrity of the anal tissue. Women who experience a traumatic delivery are at higher risk for these fissures due to the physical strain and potential injury to the anal canal.
Anal Intercourse
Anal intercourse can also contribute to the development of anal fissures. The potential for trauma or injury to the anal canal during anal intercourse can lead to fissures, especially if adequate lubrication is not used or if excessive force is applied. The sensitive tissues of the anal canal are particularly vulnerable to damage from friction and pressure, making it crucial to use lubrication and communicate openly with partners to minimize the risk of injury. Proper preparation and care during anal intercourse are essential for preventing these anal fissure causes and ensuring a safer experience.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are significant anal fissure causes. These chronic inflammatory bowel diseases can lead to ongoing inflammation and irritation of the gastrointestinal tract, including the anal canal. The persistent inflammation and ulceration associated with these conditions can weaken the anal mucosa, making it more susceptible to fissures. Managing these underlying inflammatory conditions is crucial for reducing the risk of anal fissures and improving overall anal health.
Other Contributing Factors
Several other factors can contribute to the development of anal fissures. Poor hygiene practices, such as infrequent washing of the anal area, can lead to irritation and increased vulnerability to fissures. Certain medications, especially those that affect bowel function or cause dryness, can also exacerbate the risk. Additionally, genetic predisposition may play a role in predisposing individuals to anal fissures. Addressing these contributing factors is important for comprehensive prevention and treatment of anal fissures.
Understanding these common anal fissure causes helps in identifying and addressing the underlying issues, leading to more effective management and prevention of anal fissures. By recognizing the specific factors contributing to the development of anal fissures, individuals can implement targeted strategies to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence.
Risk Factors
Age and Gender
Age and gender significantly influence the likelihood of developing anal fissures. Anal fissures are more commonly observed in women and older adults due to various anal fissure causes. For women, hormonal changes and childbirth can increase the risk of anal fissures, as previously discussed. Older adults are more susceptible to anal fissures because of the natural weakening of tissues and decreased skin elasticity that occurs with aging. Additionally, older individuals are more likely to experience chronic constipation, which is a major contributor to anal fissures.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors play a crucial role in the risk of developing anal fissures. A diet low in fiber can significantly contribute to anal fissure causes, as fiber helps maintain regular bowel movements and soft stool consistency. Inadequate hydration exacerbates this issue by causing the stools to become hard and dry, increasing the likelihood of fissures. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle contributes to constipation and poor bowel function, further elevating the risk of anal fissures. To reduce the risk, it’s essential to adopt a lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet rich in fiber, and adequate hydration to maintain optimal bowel health and prevent anal fissures.
Pre-existing Health Conditions
Pre-existing health conditions can significantly increase the risk of anal fissures. Chronic diseases that affect bowel function or lead to inflammation are common anal fissure causes. Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and other inflammatory bowel diseases contribute to persistent inflammation and irritation in the gastrointestinal tract, including the anal canal. Additionally, chronic health issues like diabetes and immune disorders can impact bowel function and the healing process, making individuals more susceptible to anal fissures. Effectively managing these underlying health conditions is vital for reducing the risk of anal fissures and improving overall anal health.
Prevention Tips
Recommendations for Maintaining Bowel Health
To prevent anal fissures, it is essential to maintain optimal bowel health. Here are some key recommendations:
- Diet: Incorporate a diet rich in fiber to promote healthy bowel movements. Foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can help keep stools soft and regular. Fiber aids in preventing constipation, which is a primary cause of anal fissures.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated. Adequate hydration helps maintain stool softness and reduces the risk of constipation, thereby decreasing the likelihood of anal fissures.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support healthy digestion and bowel function. Exercise helps stimulate regular bowel movements and can prevent constipation. Activities like walking, jogging, or swimming are beneficial for maintaining overall gastrointestinal health.
Tips for Safe Sexual Practices and Childbirth
- Safe Sexual Practices: When engaging in anal intercourse, use ample lubrication to reduce friction and minimize the risk of trauma to the anal canal. Communicate openly with your partner to ensure comfort and avoid excessive force, which can lead to fissures.
- Childbirth: To reduce the risk of anal fissures during childbirth, consider discussing delivery options with your healthcare provider. If you are at risk of a traumatic delivery or episiotomy, your provider may offer strategies to minimize the impact on the anal area. Postnatal care that includes pelvic floor exercises can also aid in recovery.
Importance of Addressing Chronic Conditions
Addressing and managing chronic health conditions is crucial for preventing anal fissures. Conditions such as inflammatory bowel diseases (e.g., Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis) and chronic diseases that affect bowel function are significant anal fissure causes. Regular medical check-ups and adherence to treatment plans for these conditions are essential. For instance, controlling inflammation and effectively managing symptoms can significantly reduce the risk of developing anal fissures. Collaborate with your healthcare provider to address any underlying health issues and maintain optimal bowel health to prevent anal fissures.
By following these prevention tips, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing anal fissures and promote overall anal and gastrointestinal health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of anal fissures?
The primary causes of anal fissures include chronic constipation, frequent diarrhea, childbirth, anal intercourse, inflammatory conditions such as Crohn’s disease, and other contributing factors like poor hygiene or certain medications. Identifying these anal fissure causes is crucial for effective treatment and prevention.
How does chronic constipation lead to anal fissures?
Chronic constipation is a major anal fissure cause because hard, dry stools can stretch and tear the lining of the anal canal. The straining associated with bowel movements can exacerbate this trauma, leading to the development of painful anal fissures.
Can diarrhea contribute to the development of anal fissures?
Yes, frequent and loose stools can irritate the anal region, making it more susceptible to fissures. Prolonged diarrhea can cause significant irritation and inflammation, increasing the risk of anal fissure formation.
How can childbirth cause anal fissures?
Vaginal delivery can cause trauma to the anal area, especially during difficult labor or when an episiotomy is performed. This trauma can lead to the development of anal fissures, making childbirth a notable cause of this condition.
What role do inflammatory conditions play in anal fissure causes?
Inflammatory conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can contribute to anal fissures by causing chronic inflammation and irritation in the anal canal. The ongoing inflammation can weaken the anal mucosa, making it more prone to fissures.
How can I prevent anal fissures?
To prevent anal fissures, focus on maintaining healthy bowel habits by consuming a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise. Additionally, practicing safe sexual activities, addressing chronic conditions, and maintaining good hygiene can help reduce the risk of anal fissures.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the causes and risk factors of anal fissures are essential for effective prevention and management. By recognizing the common anal fissure causes and taking proactive measures—such as maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, practicing safe sexual activities, and managing chronic conditions—you can significantly reduce your risk of developing anal fissures.
If you’re experiencing symptoms of anal fissures or have concerns about your digestive health, don’t hesitate to reach out to Gutcare Hospitals in Bangalore. Our experts are here to provide comprehensive care and support. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward better health.